Creating Private Audio Zones: Targeted Sound Technology Unveiled
Imagine a world where you can listen to music or podcasts without headphones, or have private conversations in public without anyone eavesdropping. Researchers have developed a groundbreaking technology that creates localized pockets of sound, effectively isolating audio within a specific area.
This innovation, termed "audible enclaves," has the potential to transform entertainment, communication, and spatial audio experiences by delivering sound only where it's needed.
The Science Behind Audible Enclaves
Sound, a vibration traveling through air as a wave, is traditionally difficult to control due to a phenomenon called diffraction. Diffraction causes sound waves to spread, especially low-frequency sounds, making it hard to confine audio to a specific location. While technologies like parametric array loudspeakers exist, they emit sound along their entire path.
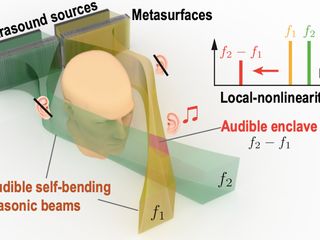
The new approach utilizes self-bending ultrasound beams and nonlinear acoustics. Ultrasound, sound waves beyond human hearing, act as a carrier for audible sound. The trick lies in the nonlinear interaction of intense sound waves. When two ultrasound beams at different frequencies intersect, they generate a new, audible frequency only at the intersection point.
Acoustic metasurfaces, specialized materials, bend ultrasound beams, allowing them to navigate around obstacles and converge at a precise target location. This "difference frequency generation" ensures that sound is only audible where the beams cross, creating a private audio zone.
Potential Applications
The applications of audio enclaves are vast. Museums could offer personalized audio guides without headphones, libraries could allow students to study with audio lessons without disturbing others, and cars could enable passengers to enjoy music without distracting the driver.
Furthermore, offices and military settings could benefit from localized speech zones for confidential conversations, and noise cancellation could be targeted to specific areas, improving focus in workplaces or reducing noise pollution in cities.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the technology holds immense promise, challenges remain. Nonlinear distortion can affect sound quality, and power efficiency needs improvement. Converting ultrasound to audible sound requires high-intensity fields, which can be energy-intensive.
Despite these hurdles, audio enclaves represent a paradigm shift in sound control, opening doors to immersive, efficient, and personalized audio experiences.
Source: Gizmodo